Reduced production lowers the. Statins decrease the low-density lipoprotein as well as total cholesterol level.
 Pharmacological Actions Of Statins A Critical Appraisal In The Management Of Cancer Pharmacological Reviews
Pharmacological Actions Of Statins A Critical Appraisal In The Management Of Cancer Pharmacological Reviews
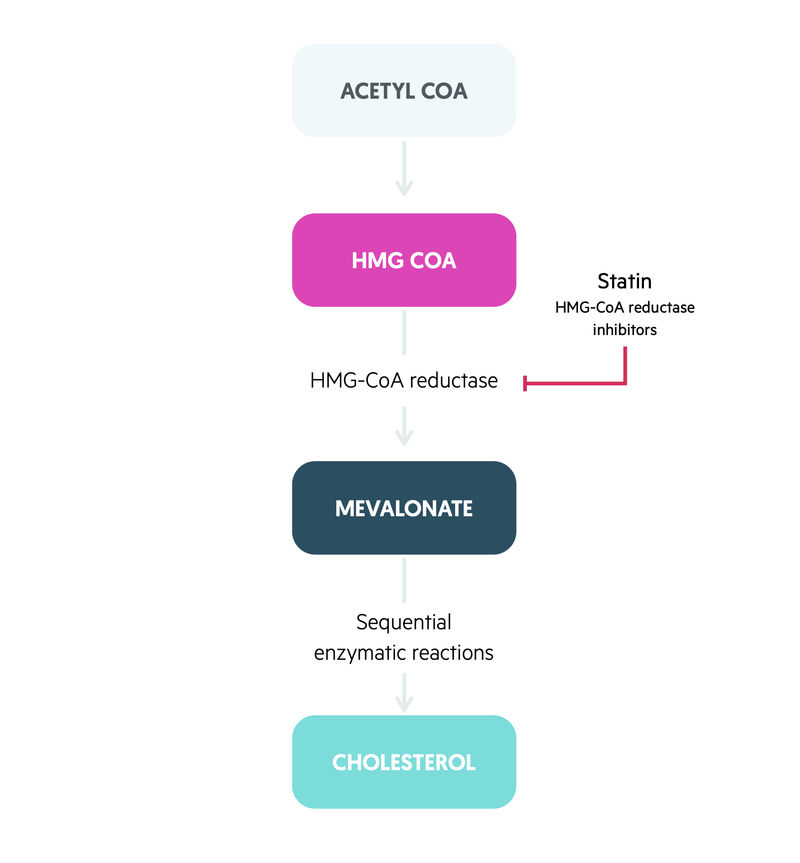
First statins block the enzyme that creates cholesterol.
Statin mechanism of action. Statins such as simvastatin and atorvastatin are used in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia act by inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A HMG-CoA reductase the enzyme that. Statins have antiatherosclerotic effects that positively correlate with. An overview on the mechanism of action of statins.
Too much deposition of the cholesterol in the walls of the arteries can build-up the plaque. Atorvastatin Lipitor competitively inhibit HMG coenzyme A reductase a rate-limiting step in cholesterol synthesis. Hepatocytes take up from the circulation 50 of LDL cholesterol.
Statins can reduce the amount of low-density lipoprotein LDL. Reduce cholesterol synthesis results in a compensatory increase in uptake of plasma cholesterol mediated by an increase in the number of LDL receptors. These bio-molecular effects of fibrates are entirely due to their capacity to activate PPAR alpha and to induce the over expression of genes containing a PPRE in their promoter.
Statin is inhibiting the HMG CoA reductase and reduce the synthesis of cholesterol. This sort animated video illustrates the mechanism of action of HMG CoA reductase enzyme inhibitors known as statins. However recent findings have indicated the inhibition of HMGCoAR as a key mechanism.
They are indicated for the treatment. Statins primarily act by lowering cholesterol production in the liver by inhibiting the action of the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase that plays a major role in cholesterol synthesis. Therefore LDL level in plasma reduces.
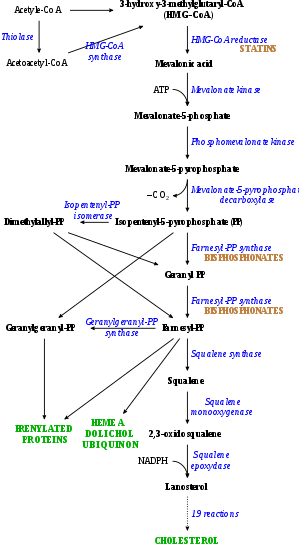
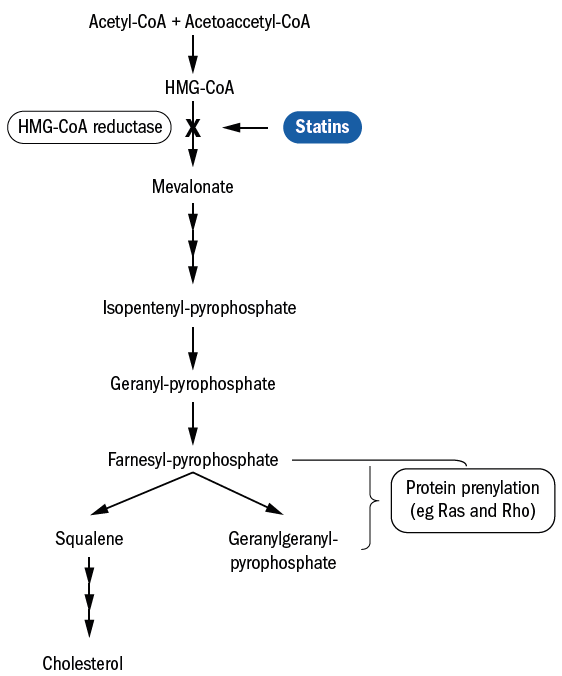
This is the principal mechanism of action of the most popular and most effective of the cholesterol-blocking medicines the HMG CoA reductase inhibitors which are collectively known as statins There is a whole family of statins see Panel 14 that because of variations in their molecular structures produce their therapeutic effects in slightly different ways. The beneficial effects of statins are the result of their capacity to reduce cholesterol biosyntesis mainly in the liver where they are selectively distributed as well as to the modulation of lipid metabolism derived from their effect of inhibition upon HMG-CoA reductase. Statins stop the production of cholesterol.
They are therefore also called also HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Therefore the mechanism of action of the statins and fibrates depends on their capacity to modulate the expression of genes controlling the lipoprotein metabolism. Mechanisms for the action of statins Mechanisms involving lipids Dyslipidemia and hypercholesterolemia are controled by the liver.
One of the main protective mechanisms elicited by statin administration is the increase in nitric oxide bioavailability that regulates cerebral perfusion and improves endothelial function but others include antioxidant properties the inhibition of inflammatory responses immunomodulatory actions the regulation of progenitor cells and the stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques. These drugs block the action of a liver enzyme that helps produce cholesterol. Statins mechanism of action Statins block the action of a liver enzyme known as HMG-CoA reductase which is responsible for producing cholesterol.
HMG CoA reductase inhibitorsor statins are widely prescribed drugs. They are also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. These hypolipidemic drugs are introduced in 1980.
Inhibition of HMG CoA reductase. Statins are thought to decrease cells uptake of glucose from the bloodstream in response to the hormone insulin. Statins work in two ways to reduce your cholesterol numbers.
An increase in the activity of LDL receptor in hepatocytes could be an efficient method to decrease plasma LDL cholesterol level. Statins have antiatherosclerotic effects that positively correlate with. The beneficial effects of statins are the result of their capacity to reduce cholesterol biosyntesis mainly in the liver where they are selectively distributed as well as to the modulation of lipid metabolism derived from their effect of inhibition upon HMGCoA reductase.
The exact mechanism responsible for the possible increased risk of diabetes mellitus associated with statin use is unclear. Common mechanism of action statins it inhibits the conversion of HMG CoA to mevalonate mevalonate is used to synthesis of cholesterol the precursor of cholesterol through HMG COA reductase.
 Myotoxicity Of Statins Mechanism Of Action Sciencedirect
Myotoxicity Of Statins Mechanism Of Action Sciencedirect
 Statins Rationale Mode Of Action And Side Effects Sciencedirect
Statins Rationale Mode Of Action And Side Effects Sciencedirect
 Immune Modulatory Effects Of Statins Zeiser 2018 Immunology Wiley Online Library
Immune Modulatory Effects Of Statins Zeiser 2018 Immunology Wiley Online Library
 Statin Toxicity Circulation Research
Statin Toxicity Circulation Research
 The Mechanism Of Action Of Statins On The Mevalonate Pathway Statins Download Scientific Diagram
The Mechanism Of Action Of Statins On The Mevalonate Pathway Statins Download Scientific Diagram
 Mechanism Of Action Of Statin And Decrease In Insulin Secretion Download Scientific Diagram
Mechanism Of Action Of Statin And Decrease In Insulin Secretion Download Scientific Diagram
 Cholesterol Lowering Drugs Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
Cholesterol Lowering Drugs Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
 Mechanism Of Action Of Statins Youtube
Mechanism Of Action Of Statins Youtube
 Hmg Coa Reductase Inhibitors Statins Mechanism Of Action Gpat Niper Pharmacist Di Exam Youtube
Hmg Coa Reductase Inhibitors Statins Mechanism Of Action Gpat Niper Pharmacist Di Exam Youtube
Http Home Sandiego Edu Josephprovost Statin 20review Pdf