A redwood tree and a dandelion both have cell walls on the outside of all of their cells. The role of a cell membrane is to monitor what exits and enters the cell and therefore.
 Ch2 Sec4 Looking Inside Cells Key Concepts What Role Do The Cell Wall And Cell Membrane Play In The Cell What Are The Functions Of Cell Organelles Ppt Download
Ch2 Sec4 Looking Inside Cells Key Concepts What Role Do The Cell Wall And Cell Membrane Play In The Cell What Are The Functions Of Cell Organelles Ppt Download
The cell membrane is inside the CM.
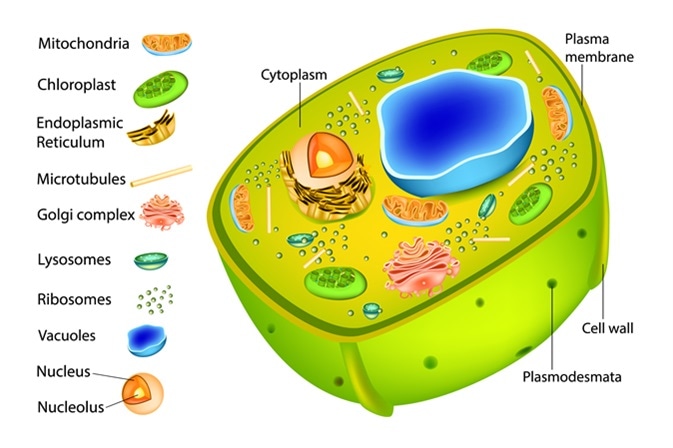
What role do cell walls play in a plant. The cell wall is the outside lining of the cell that helps hold the cell together. Cells in plant leaves produce starch in the presence of sunlight. Unlike the cell wall the cell membrane is present in all living organisms including plants.
They convert solar energy into chemical energy through photosysthesis. The cell wall is the outermost layer in a plant cell. The cell wall makes plants rigid and less flexible.
See the article Cell Membrane Surface Potential ps0 Plays a Dominant Role in the Phytotoxicity of Copper and Arsenate in Plant Physiol volume 148 on page 2134. What role do cell walls play in a plant. They are found in plants bacteria fungi algae and some archaea.
At the cellular level vacuoles play an important role in waste management. At the simplest level the walls provide a physical barrier between pathogens and the internal contents of plant cells. Forming the interface between adjacent cells plant cell walls often play important roles in intercellular communication.
It is primarily made up of carbohydrates like pectin cellulose and hemicellulose. Because of their surface location plant cell walls play an important role in plant-microbe interactions including defense responses against potential pathogens. The cell walls are there to.
The main role of the cell membrane is to provide protection to the cell from its surroundings. A cell wall provides an additional layer of protection on top of the cell membrane. The formation of the cell wall is guided by microtubules.
Microtubules have long been known to play a key role in plant cell morphogenesis but just how they fulfill this function is unclear. It also filters the molecules passing in and out of the cell. Animal cells do not have a cell wall.
The cell wall in plants is composed mainly of cellulose and contains three layers in many plants. Some plant roots and embryos in the form of seeds and fruit also serve as storage units for starch. Cell membrane Plant cell.
Combined with turgor pressure keeps the plants upright what keeps flower stems for example from wilting. However there has been a paucity of genetic evidence supporting the idea that variation in cell wall composition plays a role in the outcome of hostpathogen interactions. The most important role that cell walls play in a plant is their rigidity.
A plant cell has a cell wall whereas an animal cell only has a cell membrane. It is found in plants algae fungi prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is important to remember the following.
It provides structural support and rigidity for the plant body. Transverse microtubules have been thought to constrain the movement of cellulose synthase complexes in order to generate transverse microfibrils that are essential for elongation growth. It allows plants to support structures such as leaves and flowers due to the pressure of the central vacuole.
Wall stress relaxation reduces cell turgor and thereby creates the driving forces needed for water uptake by growing cells. It is the key physical process limiting cell enlargement Cosgrove 1997. A cell wall gives protection support and shape to a cell Why are chloroplasts important.
These negative charges create a surface electrical potential PS0 which affects ion concentrations. Almost all cell membrane surfaces CMS are intrinsically negatively charged. The cell wall is an outer protective membrane in many cells including plants fungi algae and bacteria.
A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. The high molecular weight polysaccharides that are the principal components of cell walls are crosslinked by both ionic and covalent bonds into a network that resists physical penetration 1. What is the function of the cell membrane.
And has the quality of being semi-permable so it can allow various substances to go in and out of the cell. In some plants starch is stored in cell organelles called amyloplasts. The pliancy of growing walls is special in that it enables prolonged wall extension creep and stress relaxation.
The main functions of the cell wall are to provide structure support and protection for the cell. Cell membrane cell wall. The central Vacuole in a plant cell is one of the largest cell organelles.
Recently several genetic studies have provided new lines of evidence implicating cell wall polysaccharides as factors in hostpathogen interactions. The plant cell wall is also involved in protecting the cell against mechanical stress and to provide form and structure to the cell.
 Plant Cell Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Plant Cell Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
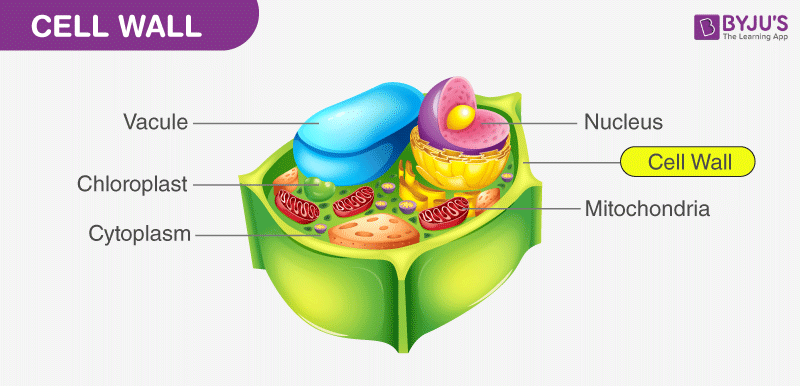 Cell Wall And Cell Membrane Structure Functions And Differences
Cell Wall And Cell Membrane Structure Functions And Differences
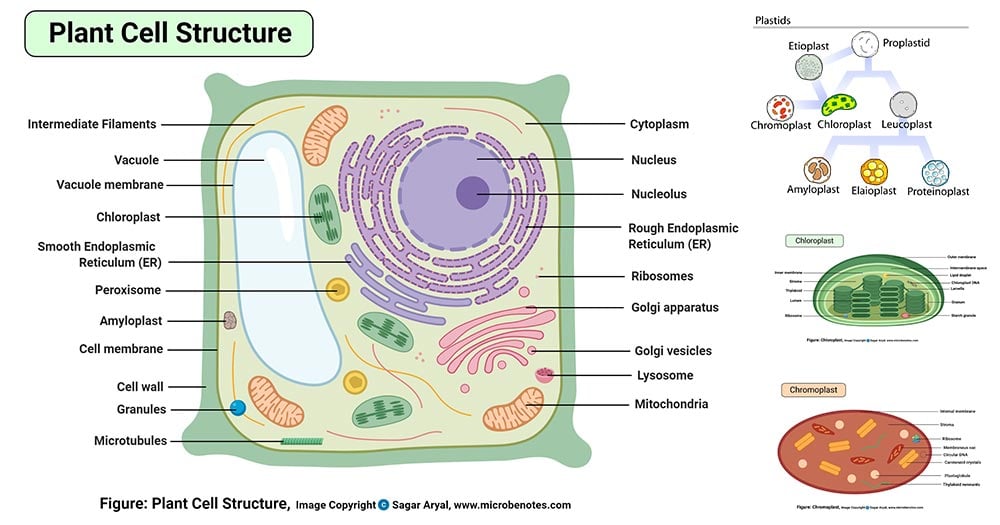 Plant Cell Definition Labeled Diagram Structure Parts Organelles
Plant Cell Definition Labeled Diagram Structure Parts Organelles
 Cell Structure And Function Ppt Video Online Download
Cell Structure And Function Ppt Video Online Download
 Do Plant Cells Have A Cell Membrane Biology Class Video Study Com
Do Plant Cells Have A Cell Membrane Biology Class Video Study Com
 Plant Cell Wall Function Structure Composition Biology Class Video Study Com
Plant Cell Wall Function Structure Composition Biology Class Video Study Com
 Plant Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Plant Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
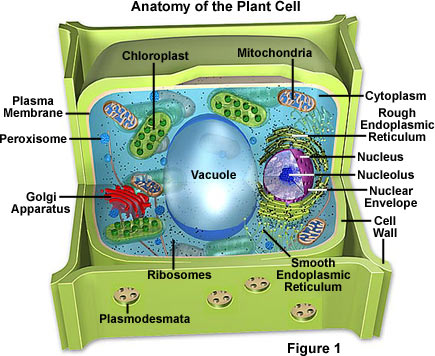 Molecular Expressions Cell Biology Plant Cell Structure
Molecular Expressions Cell Biology Plant Cell Structure
/plant_cell_wall_chloroplasts-5b64a485c9e77c0025a39acf.jpg) Cell Wall Structure And Function
Cell Wall Structure And Function
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Plant_cell_wall_diagram-en.svg-58a8766c3df78c345bdc5df3.png) Cell Wall Structure And Function
Cell Wall Structure And Function
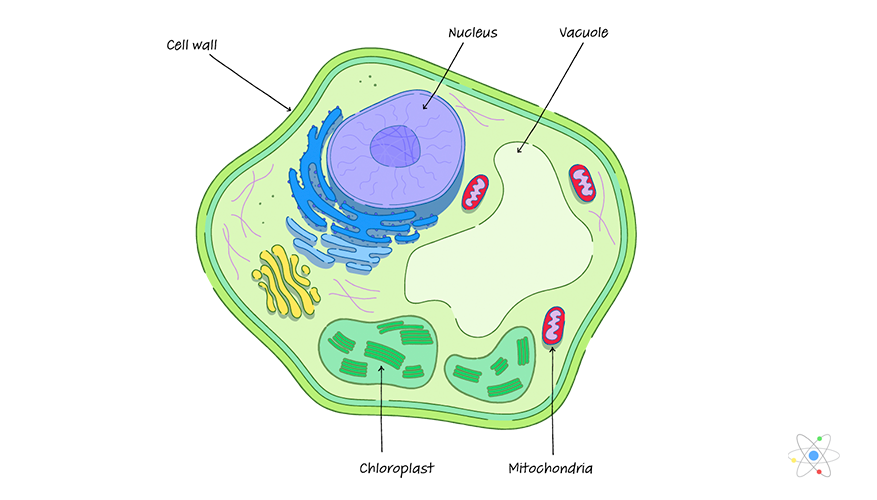 Cell Wall Definition Structure Function With Diagram
Cell Wall Definition Structure Function With Diagram
 Cell Wall Description Properties Components Communication Britannica
Cell Wall Description Properties Components Communication Britannica
