At that point the C. We studied prospectively 266 adult out-patients in the Paris France area who were prescribed a 5-10-day course of.
 Clostridium Difficile An Intestinal Infection On The Rise Harvard Health
Clostridium Difficile An Intestinal Infection On The Rise Harvard Health
Can be either directly or indirectly hospital acquired nosocomial or community acquired.

How is c diff acquired. There are several factors that can throw off the balance of gut flora but the one most commonly linked to Cdiff infection is taking antibiotics. Thus these spores survive in clinical environments for long periods. Environmental contamination has been associated with the spread of C.
Replacement of electronic thermometers with single-use disposable thermometers has been associated with significant decreases in CDI incidence 243. Clostridium difficile also known as C. Signs and symptoms of severe infection include.
Difficile is commonly known as a hospital and antibiotic associated pathogen at most one third of infections can be traced to transmission from an infected person in hospitals and only a small number of antibiotics are directly associated with an elevated risk of developing a C. People who have a severe C. Advanced probiotics are currently being studied for their potential use in C.
Most cases of C. It can spread easily to others. Research hasnt consistently shown that currently available products are helpful in preventing or treating infection with C.
Clostridium difficile or C. Difficile can cause the colon to become inflamed and sometimes form patches of raw tissue that can bleed or produce pus. That means that they can be transferred when one infected person simply touches another person.
Clostridium difficile is the main cause of nosocomial infectious diarrhoea and the causative agent of antibiotic-associated colitis. Diff is bacteria that can infect the bowel and cause diarrhoea. Difficile infection CDI namely clindamycin fluoroquinolones and cephalosporins.
It is therefore also called antibiotic-associated colitis. Difficile infection are particularly high among hospitalized patients and residents in long-term care facilities because C. Diff colitis is a common infection of the colon that is typically associated with the use of antibiotics.
The organism forms heat-resistant spores that are not killed by alcohol-based hand cleansers or routine surface cleaning. Typically community-acquired infections occur in younger age-groups than hospital-acquired CDI often in the absence of obvious risk factors. Difficile is transmitted from person to person by the fecal-oral route.
The infection most commonly affects people who have recently been treated with antibiotics. Because of this the bacteria may be cultured from almost any surface. Difficile infection in antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in the community is poorly documented.
Difficile infection is controversial. Recent stay at a hospital or nursing home. Because those affected generally have fewer comorbidities the overall mortality is lower than that of hospital-acquired infection but up to 40 of patients with community-acquired CDI require admission to hospital and rapidly progressive severe disease can occur in previously healthy young people 5 10.
Difficile infection tend to become dehydrated and may need to be hospitalized. Diff can colonize out of control making the infected person much sicker. Diff bacteria that are outside the body turn into spores that can live on surfaces for weeks.
Diff infection occurs when theres too much of the bacterium in your intestines. Spores transmitted from others and patients by hands or altered normal intestinal flora by antibiotic therapy allowing proliferation of Cdiff. Difficile treatment or prevention but arent currently available.
3 Superbugs are invisible and can survive on surfaces for days to weeks. There are other risk factors. However other bacteria that live in the intestines usually keep the amount of C.
The involvement of C. Diff is a germ that causes serious diarrhea and other problems. Formerly known as Clostridium difficile is a gram-positive bacillus that may cause antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Clostridium is a family of bacteria containing several members. Diff exists all around us. Diff occur when youve been taking antibiotics or not long after youve finished taking antibiotics.
Diff infections tend to occur when there is an imbalance of bacteria in the human gut which allows Cdiff to grow and release toxins. It can be caused by taking antibiotics. Being 65 or older.
Another common name for this condition is pseudomembranous colitis. Difficile spores are easily transmitted fecal-oral. Mode of transmission of C.
Difficile via contaminated commodes blood pressure cuffs and oral and rectal electronic thermometers 74 241 242. Watery diarrhea 10 to 15 times a day. The role of these products in C.
Diff can infect anyone. Its in the air water soil and in the feces of humans and animals. Author Shelley Johnson 1 Affiliation 1 Shelley Johnson is the director of critical care services at NorthBay Healthcare in Fairfield Calif.
 Understanding Clostridium Difficile Colonization Clinical Microbiology Reviews
Understanding Clostridium Difficile Colonization Clinical Microbiology Reviews
 Reducing Hospital Acquired C Diff Saves Over 800k
Reducing Hospital Acquired C Diff Saves Over 800k
 Reducing Hospital Acquired C Diff Saves Over 800k
Reducing Hospital Acquired C Diff Saves Over 800k
 Clostridioides Difficile Characteristics Disease And Laboratory Diagnosis Learn Microbiology Online
Clostridioides Difficile Characteristics Disease And Laboratory Diagnosis Learn Microbiology Online
 C Difficile Infection A Hospital Acquired Disease Youtube
C Difficile Infection A Hospital Acquired Disease Youtube
 Clostridium Difficile Infection Nursing Considerations
Clostridium Difficile Infection Nursing Considerations
Reducing Hospital Acquired Clostridium Difficile On A Medical Renal Unit Ihi Institute For Healthcare Improvement
 Clostridioides Difficile Infection Hai Cdc
Clostridioides Difficile Infection Hai Cdc
 Medical Cleaning Challenge C Diff Summit Janitorial Services
Medical Cleaning Challenge C Diff Summit Janitorial Services
 Update On Treatment Of Clostridioides Difficile Infection Mayo Clinic Proceedings
Update On Treatment Of Clostridioides Difficile Infection Mayo Clinic Proceedings
 Pdf Clostridium Difficile Found In Gardening Products Innocent Bystander Or The Cause Of Community Acquired C Difficile Infection Through Contamination Of Foods And Environments
Pdf Clostridium Difficile Found In Gardening Products Innocent Bystander Or The Cause Of Community Acquired C Difficile Infection Through Contamination Of Foods And Environments
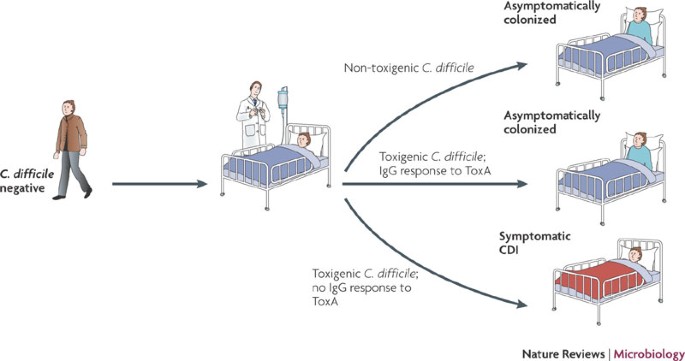 Clostridium Difficile Infection New Developments In Epidemiology And Pathogenesis Nature Reviews Microbiology
Clostridium Difficile Infection New Developments In Epidemiology And Pathogenesis Nature Reviews Microbiology
 Faqs For Clinicians About C Diff Cdc
Faqs For Clinicians About C Diff Cdc
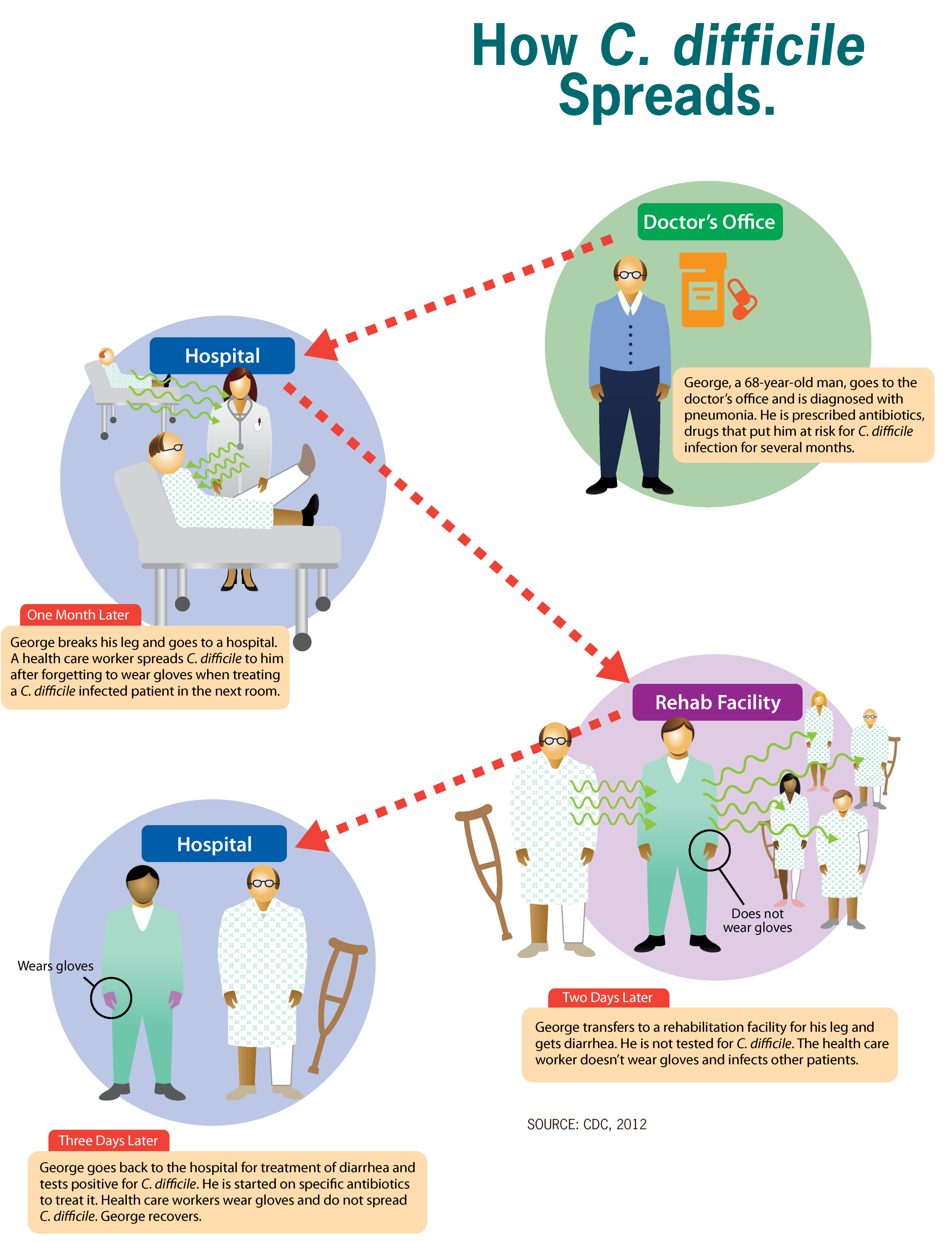 Disease Outbreak Control Division Clostridioides Difficile Infections C Diff Cdi
Disease Outbreak Control Division Clostridioides Difficile Infections C Diff Cdi