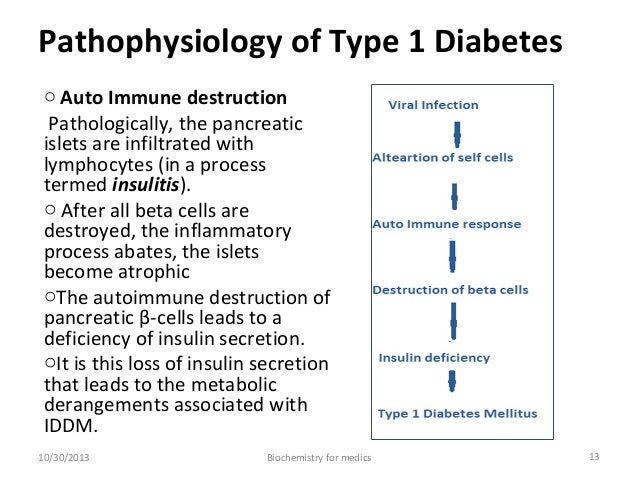
The pathophysiology of all types of diabetes is related to the hormone insulin which is secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas. Advances in management of type 1 diabetes mellitus.
The condition is usually diagnosed in children and young.
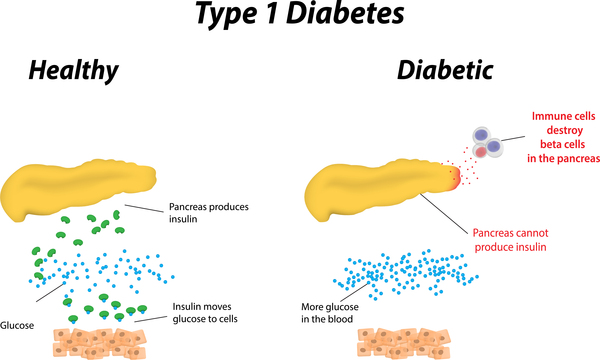
Pathophysiology of juvenile diabetes. Can Type 1 Diabetes treatments be applied successfully to Type 2 Diabetes. Only 5 of people with diabetes have this form of the disease. Aathira R Jain V.
Type 1 diabetes once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Type 1 diabetes is a condition in which your immune system destroys insulin -making cells in your pancreas. As the name suggests the disease is commonly diagnosed in childhood or adolescence as opposed to.
Non-type 1 diabetes is recognised with increasing frequency particularly emerging molecular forms of diabetes diabetes secondary to pancreatic disease and a rise in type 2 diabetes and other insulin resistance syndromes in the young. Before treatment this results in high blood sugar levels in the body. It is also called Type I diabetes or a special case of Type I Diabetes Mellitus.
It develops when the bodys immune system destroys pancreatic beta cells the only cells in the body that make the hormone insulin which regulates blood glucose. Insulin is a hormone required for the body to use blood sugar. Type 1 diabetes Type 1 diabetes in children previously called juvenile diabetes occurs when the.
It is also the study of the manifestations of diabetes and the abnormalities resulting from physical and biological disturbances caused by the disease. The pathophysiology of diabetes involves plasm concentrations of glucose signaling the central nervous system to mobilize energy reserves. Are Type 1 Diabetes symptoms the same as Type 2 Diabetes symptoms.
This condition is known to occur at any age group but the majority of affected individuals are diagnosed in their mid-teenage years. Type 1 diabetes T1D previously known as juvenile diabetes is a form of diabetes in which very little or no insulin is produced by the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. In a healthy person insulin is produced in response to the increased level of glucose in the bloodstream and its major role is to control glucose concentration in the blood.
Type 1 diabetes in children used to be known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes. Pathophysiology of Type 1 Diabetes in Children The main defect seen in the disease is pancreatic cell destruction from autoimmune antibodies which target the islet v-cells that secrete insulin. Although type 1 is more common in young people both types can affect children and teenagers.
Different factors including genetics and some viruses may contribute to type 1 diabetes. Juvenile diabetes is defined as the sharp rise in blood glucose level hyperglycemia in children due to pancreatic dysfunctions that leads to an acute shortage of insulin which is responsible for regulating blood glucose level. It can start when youre a grownup too.
Pathophysiology of Diabetes Type 1 Type I diabetes mellitus formerly referred to as juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Type 1 diabetes in children is a condition in which your childs body no longer produces an important hormone insulin. Insulin is a hormone needed to allow sugar glucose to enter cells to produce energy.
The destruction of pancreatic v-cells is caused by the following. The pathophysiology of diabetes refers to the changes relating to or associated with the disease diabetes. Type 1 diabetes used to be called juvenile diabetes because its usually diagnosed in children and teens.
Your child needs insulin to survive so the missing insulin needs to be replaced with injections or with an insulin pump. Juvenile diabetes is mostly an autoimmune disorder and is also referred to as type 1 diabetes. Nonimmune type 1B diabetes occurs secondary to other diseases and is much less common than autoimmune type 1A.
But dont let that old-school name fool you. Guideline Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus is a syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia and insulin deficiency resulting from the loss of beta cells in pancreatic islets Mapes Faulds 2014.
It is based on cerebral blood flow and tissue integrity arterial plasma glucose the speed that plasma glucose concentrations fall and other available metabolic fuels. These are called beta cells. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults.
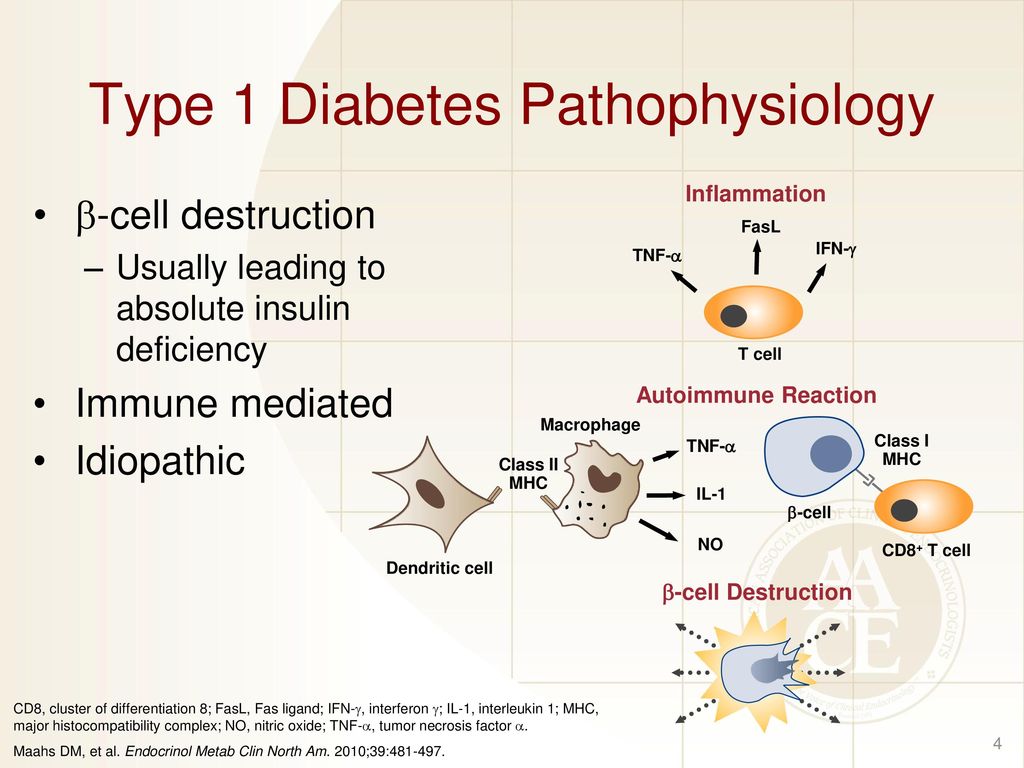 Pathophysiology Of Type 1 Diabetes Ppt Download
Pathophysiology Of Type 1 Diabetes Ppt Download
 A Schematic Diagram For Pathogenesis Of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Download Scientific Diagram
A Schematic Diagram For Pathogenesis Of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Download Scientific Diagram
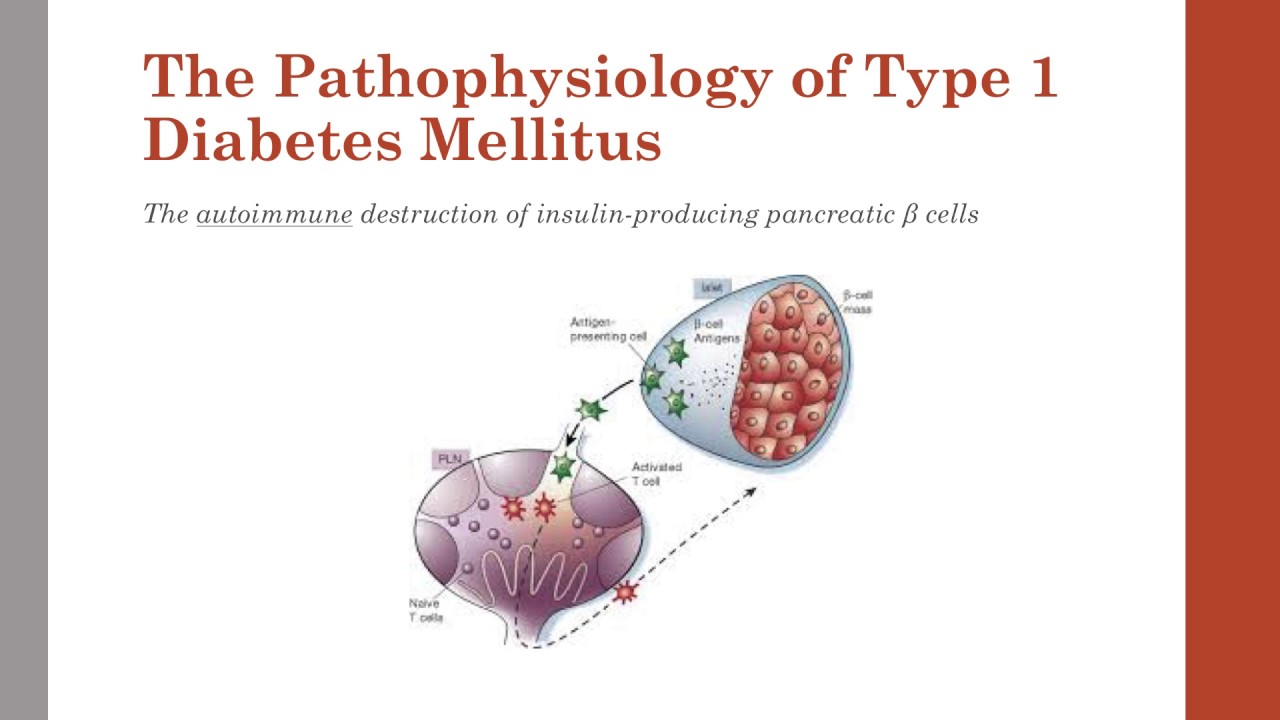 The Pathophysiology Of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Youtube
The Pathophysiology Of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Youtube
 Pathophysiology And Clinical Presentation Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Pathophysiology And Clinical Presentation Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathophysiology Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus A 90 Year Perspective Postgraduate Medical Journal
Pathophysiology Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus A 90 Year Perspective Postgraduate Medical Journal
 Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 Pathophysiology Wikidoc
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 Pathophysiology Wikidoc
 Differentiation Of Diabetes By Pathophysiology Natural History And Prognosis Diabetes
Differentiation Of Diabetes By Pathophysiology Natural History And Prognosis Diabetes
 A Schematic Diagram For Pathogenesis Of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Download Scientific Diagram
A Schematic Diagram For Pathogenesis Of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Download Scientific Diagram
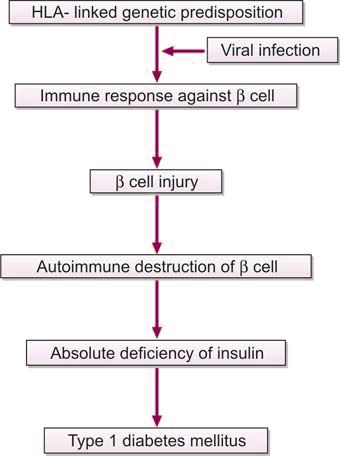 Classification Of Diabetes Mellitus
Classification Of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus Pathophysiology Herbal Management Keywords Diabetes Mellitus Hyperglycemia Metabolic Disarray Hypoglycemic Agents Herbal Formulations Doi Http Dx Doi Org 10 20510 Ukjpb 5 I5 166554 Pharmaceutical And Biosciences
 A Review On Herbs Which Are Used In Diabetes Mellitus Insight Medical Publishing
A Review On Herbs Which Are Used In Diabetes Mellitus Insight Medical Publishing
 Enteroviral Pathogenesis Of Type 1 Diabetes Didier Hober Discovery Medicine
Enteroviral Pathogenesis Of Type 1 Diabetes Didier Hober Discovery Medicine