Tetralogy of Fallot has a broad anatomical spectrum. Right ventricular outflow obstruction stenosis right ventricle hypertrophy over-riding aorta ventricular septal defect right arch in 20.
 Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Radiology Radiology Imaging Diagnostic Medical Sonography
Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Radiology Radiology Imaging Diagnostic Medical Sonography
Tetralogy of Fallot radiology discussion including radiology cases.

Tetralogy of fallot radiology. A fetus diagnosed with Tetralogy of Fallot may need surgery or other procedures soon after birth. Tetralogy of Fallot TOF is an abnormality of conotruncal formation. A demonstration in two cases was made by Castellanos Pereiras and Garcia 3 but their observations were limited to the right side of the heart and their studies made in infants exclusively.
Tetralogy of Fallot teh-TRAL-uh-jee of fuh-LOW is a rare condition caused by a combination of four heart defects that are present at birth congenital. Tetralogy of Fallot is defined by four classic elements. Tetralogy of Fallot TOF is the most common cyanotic congenital heart condition with many cases presenting after the newborn period.
Other symptoms may include a heart murmur finger clubbing and easy tiring upon breastfeeding. If tetralogy of Fallot has been repaired with surgery and theres no obstruction or leak in the pulmonary valve you may be able to participate in normal activities without much increased risk. Tetralogy of Fallot TOF is a congenital cardiovascular anomaly that consists of right ventricular outflow tract obstruction right ventricular hypertrophy high ventricular septal defect VSD and an overriding aorta.
Tetralogy of Fallot is a type of heart defect present at birth. It consists of a right ventricular outflow tract obstruction a malalignment ventricular septal defect an. Misalignment of the VSD ventricular septal defect right displacement of the aorta overriding aorta hypertrophy of the right ventricle and pulmonary stenosis PS.
Tetralogy of Fallot TOF is one of the most common cyanotic congenital heart disease with complex anatomic malformations and unknown etiology. Boot shaped heart upward pointing cardiac apex due to right ventricular hypertrophy. Symptoms at birth may vary from none to severe.
Later there are typically episodes of bluish color to the skin known as cyanosis. In mild forms of the condition the obstruction is only located in the right ventricular infundibulum whereas in severe forms the pulmonary valve is atretic the pulmonary arteries are absent and the lung is supplied by aorto-pulmonary collateral arteries. Tetralogy of Fallot TOF is one of the most common congenital heart diseases for which patients are referred for postoperative magnetic resonance MR imaging evaluation.
Here the aim is to present the ultrasound features with examples of Tetralogy of Fallot along with the story post birth in terms of surgical treatment. Approximately 90 of patients with a right aortic arch and mirror-image branching have tetralogy of Fallot. Hemodynamically the critical component of the anomaly is the right ventricular outflow tract obstruction which may come in a.
These defects which affect the structure of the heart cause oxygen-poor blood to flow out of the heart and to the rest of the body. Most common cyanotic congenital heart disease. This information was gathered doing a literature search using PubMed and the University of South Australia library database as well as through information provided by the Royal Childrens Hospital Cardiology department via fact sheets.
Tetralogy of Fallot usually is diagnosed after a baby is born often after the infant has an episode of turning blue during crying or feeding a tet spell. With medical advancements most patients in this cohort require early total correction and survive into adulthood. TOF is characterised by a ventricular septal defect VSD overriding aorta astride of the VSD and pulmonary stenosis or atresia with or without right ventricular hypertrophy.
This case shows the classic plain radiographic findings of tetralogy of Fallot. It has been classically characterized by the combination of ventricular septal defect VSD right ventricular outflow tract obstruction RVOTO overriding aorta and late right ventricular hypertrophy. No similar report has been found in the American literature.
Some findings on a physical exam may make the health care provider think a baby may have tetralogy of Fallot including bluish-looking skin or a heart murmur a whooshing sound caused by blood not flowing properly through the heart. When affected babies cry or have a bowel movement they may develop a tet spell where they turn very blue have difficulty breathing become limp and occasionally lose consciousness. You may need to limit your activity if there is leftover obstruction or a pulmonary valve leak which is common after repair.
The most common surgical procedures for TOF repair include infundibulectomy transannular pulmonary artery patch repair and right ventriclepulmonary artery conduit placement. Of patients with tetralogy of Fallot 25 have a right aortic arch and most have a mirror-image branching pattern. Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common type of cyanotic congenital heart disease.
The Tetralogy of Fallot was first described by Louis Arthur Etienne Fallot in 1888 as La Maladie Bleue It is a clinical condition created by a group of anatomical malformations with fundamental features consisting of an interventricular communication also known as ventricular septal defect biventricular connection of the aortic root overriding the muscular. Tetralogy of Fallot TOF is a congenital heart defect CHD found in 1 of 3600 live births and represents 35 to 7 of all CHDs in infants. In the following case contrast visualization was successful in establishing the pathological physiology in a case of tetralogy of Fallot.
The conotruncus consists of the muscularized conus or conal septummuscular septal tissue separating the region just beneath the great vesselsand the superiorly adjacent truncus arteriosus which eventually differentiates into the great vessels arising from the heart the pulmonary artery and aorta. Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common congenital heart disease associated with a right aortic arch.
 Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
 Imaging Of Postoperative Tetralogy Of Fallot Repair Sciencedirect
Imaging Of Postoperative Tetralogy Of Fallot Repair Sciencedirect
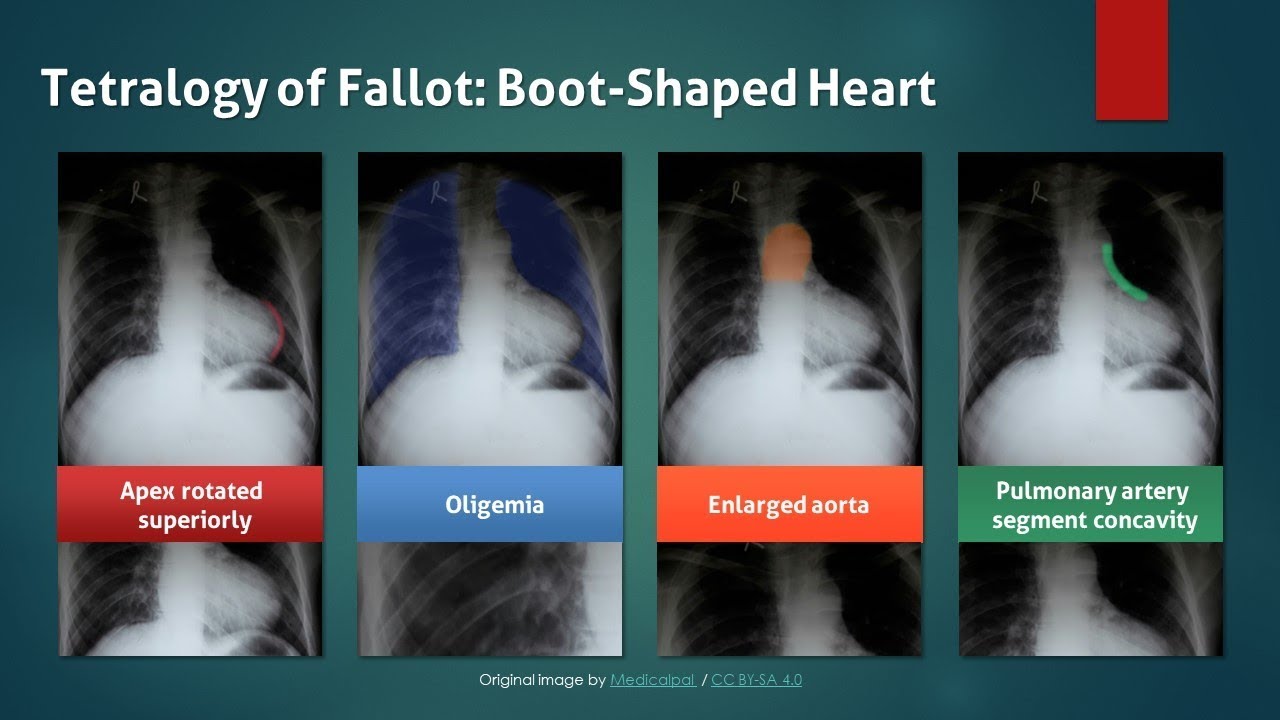 Tetralogy Of Fallot Explanation Of Chest X Ray Findings Boot Shaped Heart Youtube
Tetralogy Of Fallot Explanation Of Chest X Ray Findings Boot Shaped Heart Youtube
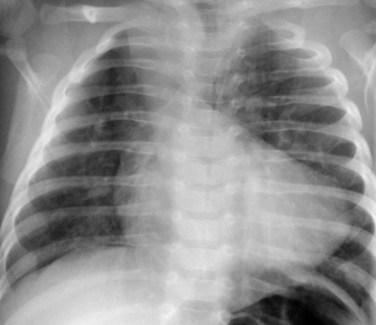 Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Key
Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Key
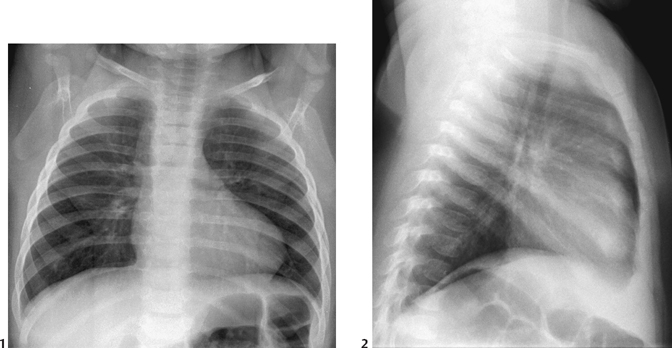 50 Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Key
50 Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Key
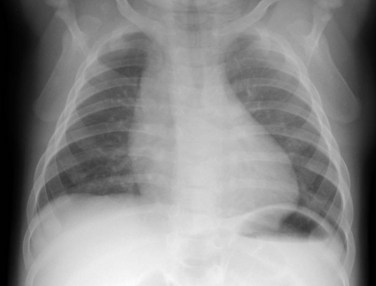 Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Key
Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Key
 Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
 An Interesting Chest X Ray Tetralogy Of Fallot Tof Tof X Ray Boot Shaped Heart Youtube
An Interesting Chest X Ray Tetralogy Of Fallot Tof Tof X Ray Boot Shaped Heart Youtube
 Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
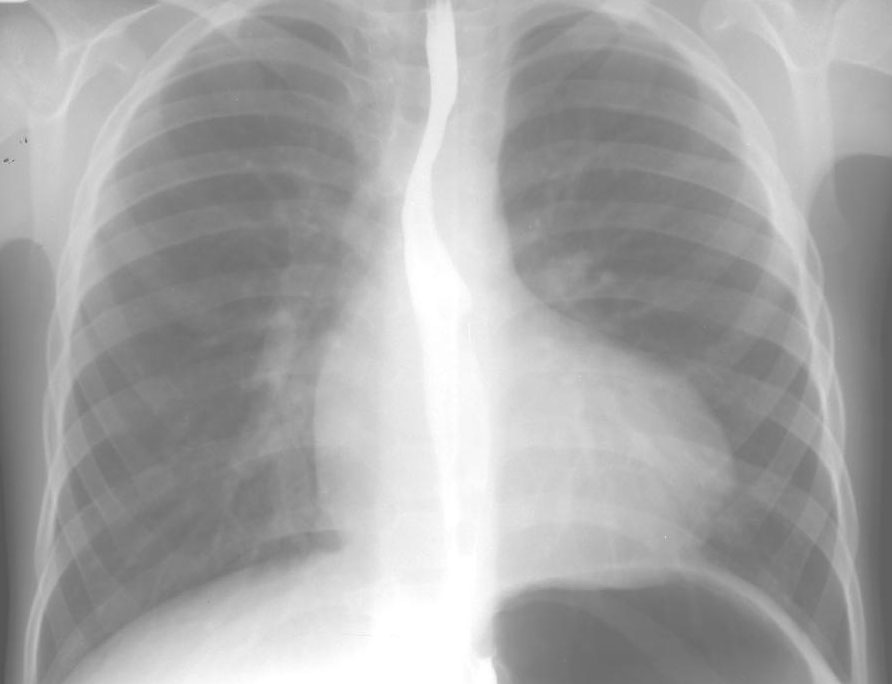 Plain Radiographic Diagnosis Of Congenital Heart Disease
Plain Radiographic Diagnosis Of Congenital Heart Disease
 Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
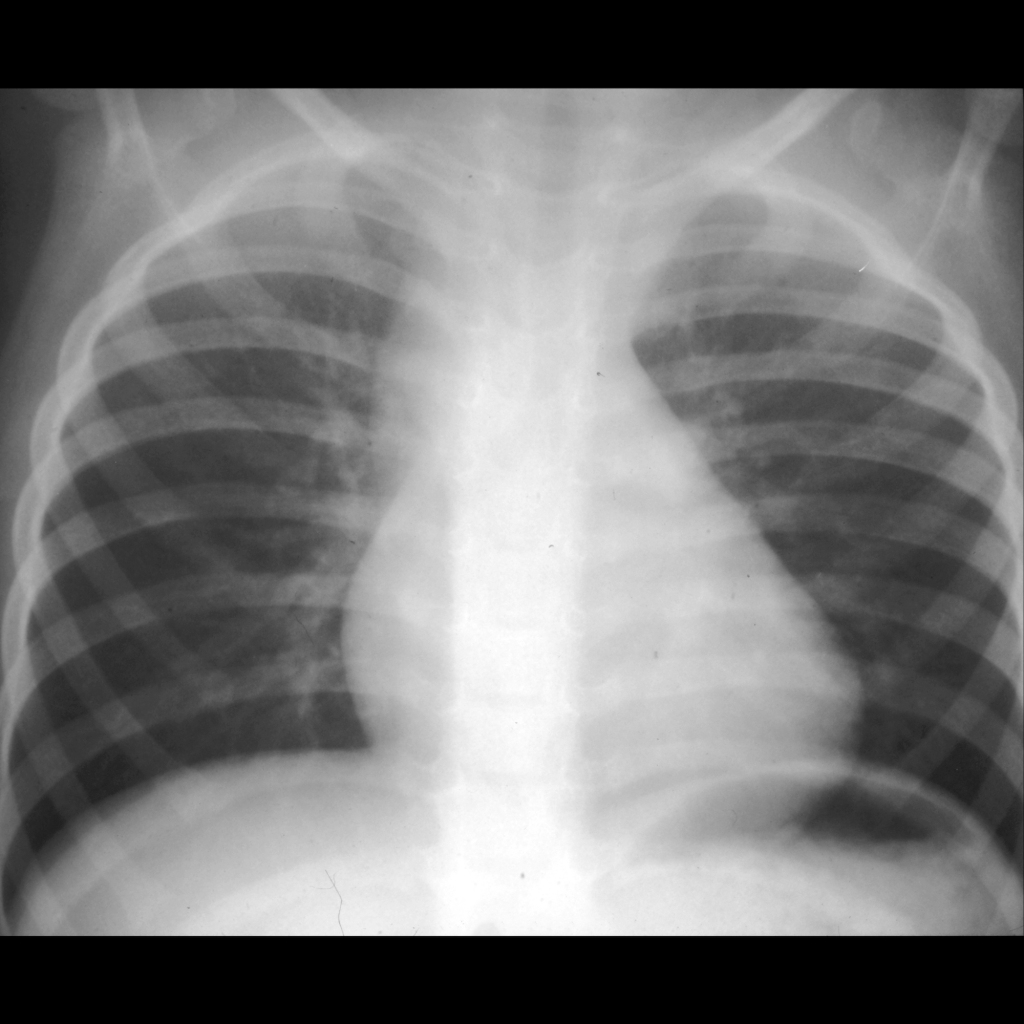 Tetralogy Of Fallot Pediatric Radiology Reference Article Pediatricimaging Org Pedsimaging
Tetralogy Of Fallot Pediatric Radiology Reference Article Pediatricimaging Org Pedsimaging
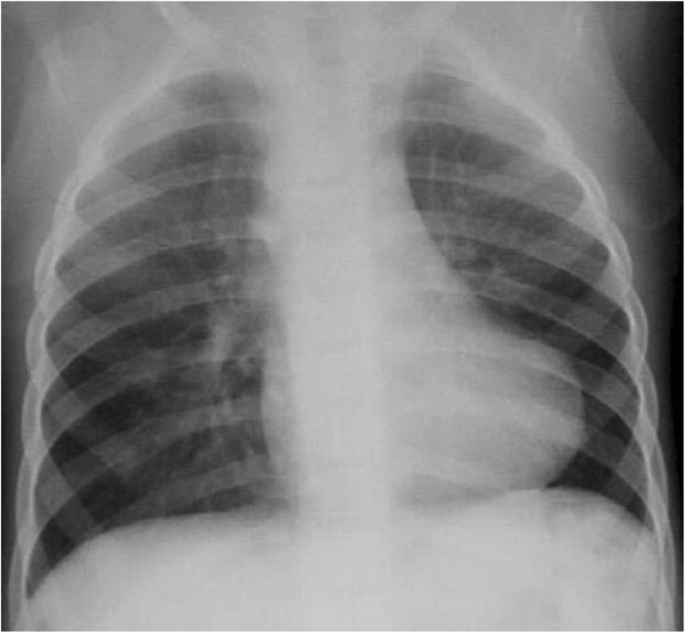 Cardiovascular Imaging Approach In Pre And Postoperative Tetralogy Of Fallot Bmc Cardiovascular Disorders Full Text
Cardiovascular Imaging Approach In Pre And Postoperative Tetralogy Of Fallot Bmc Cardiovascular Disorders Full Text
 Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Tetralogy Of Fallot Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org