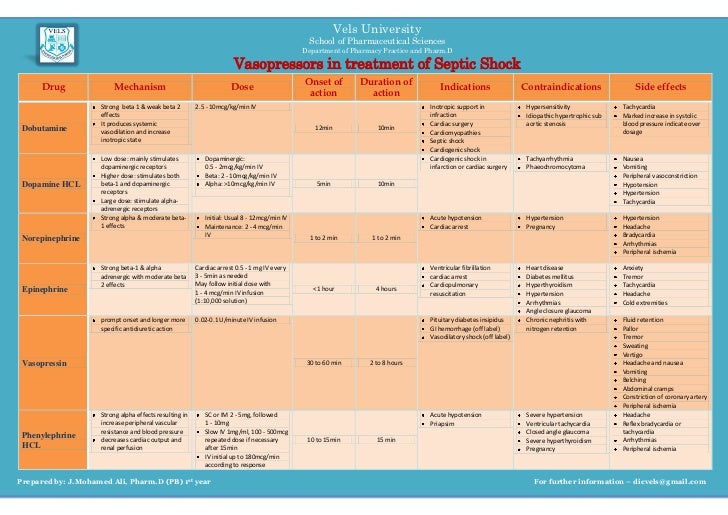
It appears safe but with a different side effect profile from norepinephrine. Vasopressin and epinephrine represent second-line vasopressor therapies and dopamine should be avoided.
 Proper Use Of Vasopressors In Septic Shock Healthmanagement Org
Proper Use Of Vasopressors In Septic Shock Healthmanagement Org
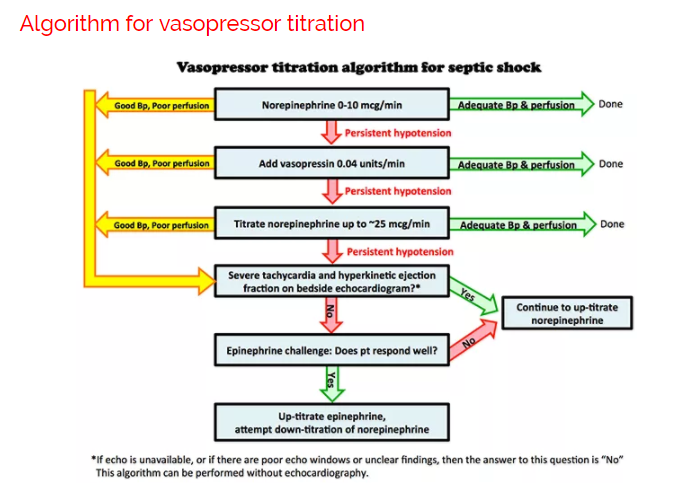
Early vasopressin NE remains the first-choice vasopressor in patients with septic shock.
Vasopressors in septic shock. In health vasopressin levels are generally less than 4 pmolL. The mortality rate reported is 40 to 60 13. Vasopressin 003 Umin added to norepinephrine appears to be as safe and effective as norepinephrine in fluid-resuscitated patients with septic shock.
From bench to bedside. Patients with septic shock is sensitive to vasopressin administration. Vasopressor and inotrope selection for cardiogenic shock follows similar physiologic principles as septic shock.
Vasopressin versus norepinephrine infusion. Vasopressin therapy in septic shock had no effect on 28-day mortality although the confidence intervals are wide. Septic shock accounts for about 9 of admissions and is the most common cause of death in intensive care units ICUs 12.
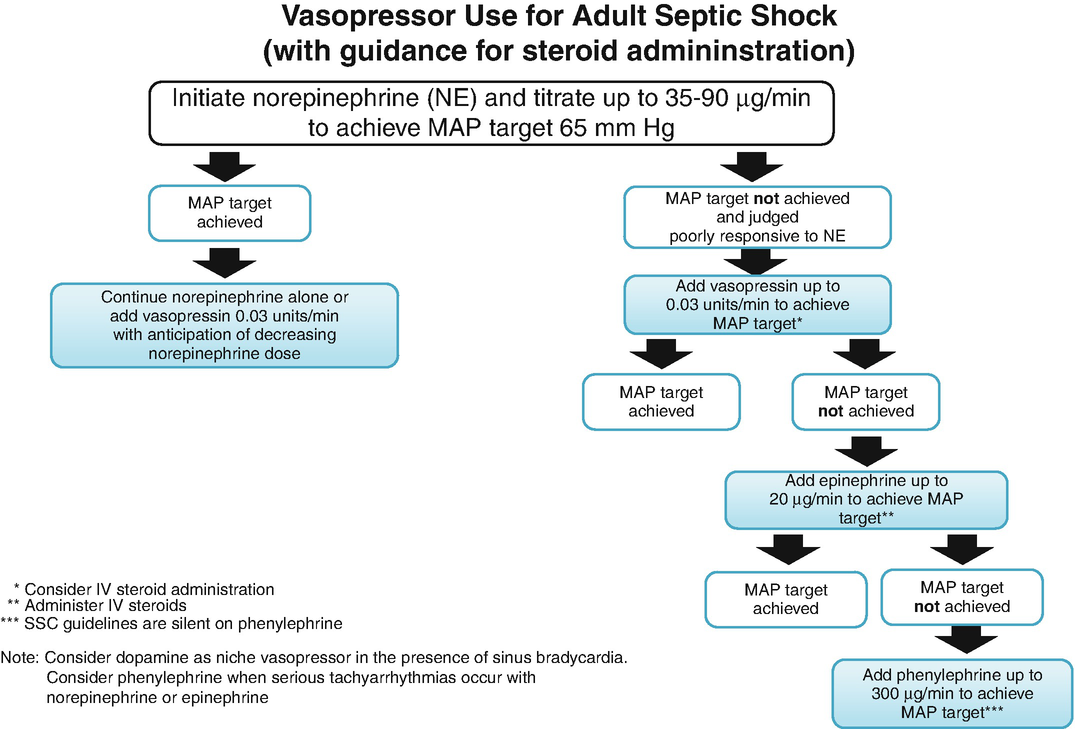
In addition to fluid resuscitation the vasopressor therapy is a fundamental treatment of septic shock-induced hypotension as it aims at correcting the vascular tone depression and then at improving organ perfusion pressure. Norepinephrine remains the first-line vasopressor in septic shock although vasopressin may be initiated with potential benefits associated with earlier initiation. There is not a single preferred vasoactive therapy with the strategy dependent upon the etiology left heart failure right heart failure outflow obstruction aortic stenosisregurgitation or mitral stenosisregurgitation and clinical presentation.
Experts recommendations currently position norepinephrine NE as the first-line vasopressor in septic shock. Septic shock is defined by the ACCPSCCM as the need for vasopressors to reverse sepsis-induced hypotension. However in shock states large increases are seen.
Taken all these evidence based on RCTs NE vs. Levy B1 Collin S Sennoun N Ducrocq N Kimmoun A Asfar P Perez P Meziani F. Very low doses of vasopressin from 001 to 005 unitsmin have been shown to improve mean arterial pressure.
Noradrenaline is the vasopressor administered most commonly to patients with distributive shock However in one study 172 of patients with septic shock in United States hospitals received vasopressin usually in combination with catecholamines In the Adjunctive Glucocorticoid Therapy in Patients with Septic Shock ADRENAL trial which included patients from Australia the United. For instance in cardiogenic shock vasopressin levels of more than 20 pmolL. High-dose vasopressin is not superior to norepinephrine in septic shock Critical care medicine 3111 2003.
Vasopressin dosages may exceed 003 units in refractory septic shock although benefits may not outweigh risks in some patients. Vasopressin levels in septic shock. Vasopressin may be more effective in patients receiving lower doses of norepinephrine than when started as rescue therapy although the answer to the question of what therapy to administer in patients with high vasopressor requirements despite vasopressin infusion remains uncertain.
Dopamine NE dobutamine vs. In addition doses above 004 unitsminute did not consistently improve hemodynamics. Septic shock is defined by persisting hypotension requiring vasopressors to maintain a mean arterial pressure of 65 mm Hg or higher and a serum lactate level greater than 2 mmolL 18 mgdL despite adequate volume.
Vascular hyporesponsiveness to vasopressors in septic shock. Klinzing Stefan et al. The effects of catecholamines range from pure a-agonist to pure v-agonist Table 2.
The finding on reduced RRT should be interpreted cautiously. Norepinephrine was used by 816 97 respondents as the first-line vasopressor in septic shock while more respondents from lower-income countries preferred a different vasopressor 6 vs. Have been reported2In contrast a relative vasopressin.
Vasopressor Administration on Mortality SUMMARY. Increasing vasopressor doses are associated with increasing mortality over the first 24 hours of septic shock. The Cardiopulmonary Effects of Vasopressin Compared With Norepinephrine in Septic Shock Cardiopulmonary Effects of VasopressinCHEST Journal 1423 2012.
1Groupe Choc Contrat Avenir INSERM 2006 Faculte de Medecine Nancy Universite 9 Avenue de la Foret de Haye BP 184 Vandoeuvre-les-Nancy Cedex 54505 France. Studies of vasopressin in adults with vasodilatory shock have used infusion rates of 001 to 01 unitsmin. Vasopressor agents should be used according to practical considerations in septic shock patients Table 1.
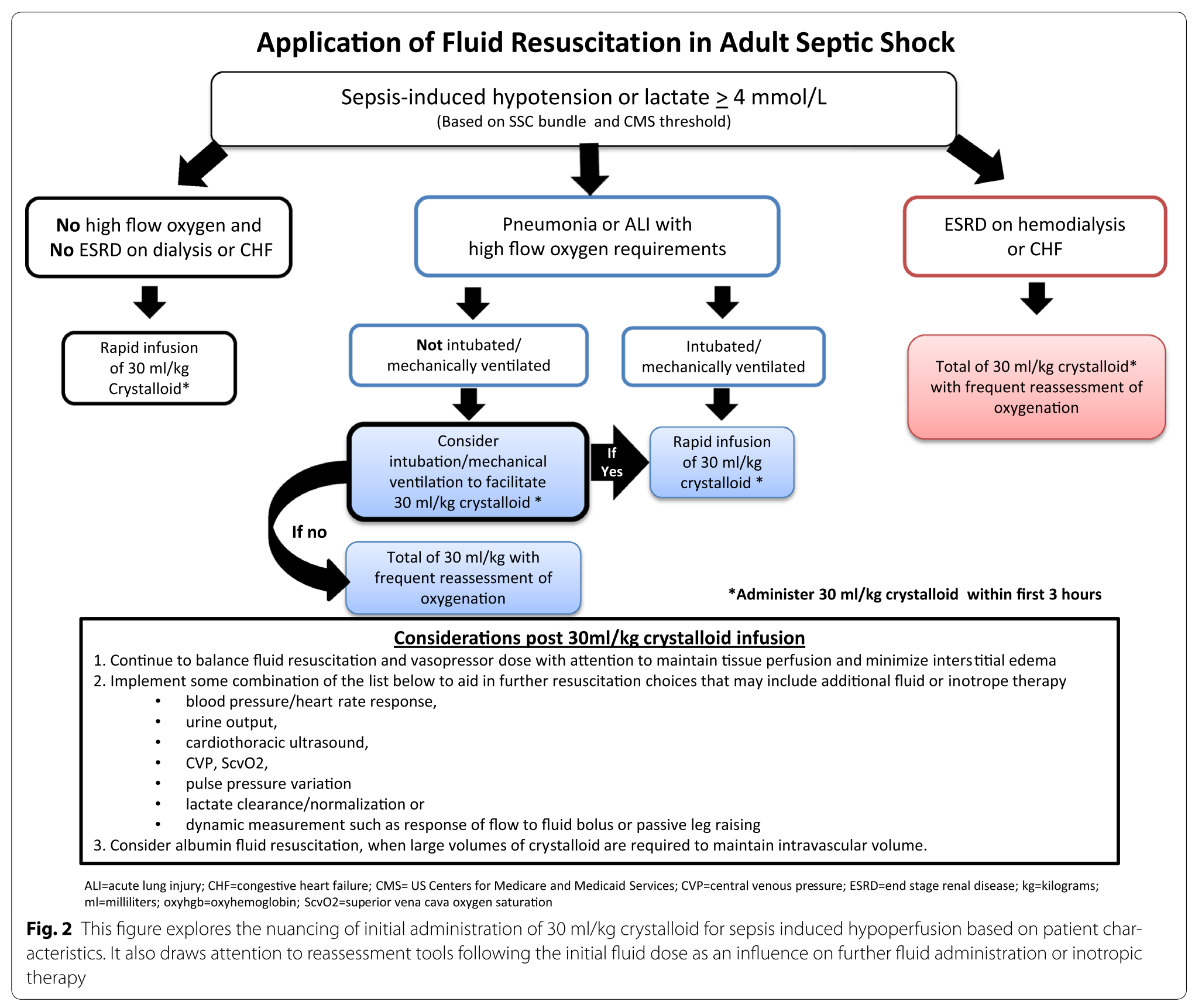
Septic shock occurs in a subset of patients with sepsis and comprises of an underlying circulatory and cellularmetabolic abnormality that is associated with increased mortality. Increasing doses of vasopressors within the first 6 hours are associated with increased mortality unless paired with at least 2000 mL of fluid administration. In addition to fluid resuscitation the vasopressor therapy is a fundamental treatment of septic shock-induced hypotension as it aims at correcting the vascular tone depression and then at.
Russell JA Walley KR Singer J Gordon AC Hebert PC Cooper DJ et al. 15 from high-income countries p 0001. The basic catecholamine structure is a phenylethylamine with three hydroxyl groups.
Vasopressin in septic shock.
 Early Norepinephrine To Stabilize Map In Septic Shock
Early Norepinephrine To Stabilize Map In Septic Shock
 Shock Lesson 5 Pressors Youtube
Shock Lesson 5 Pressors Youtube
 Rotation Prep Nejm Resident 360
Rotation Prep Nejm Resident 360
Vasopressors For Septic Shock Emergency Medicine Kenya Foundation
 Accelerated Goal Directed Therapy For Septic Shock
Accelerated Goal Directed Therapy For Septic Shock
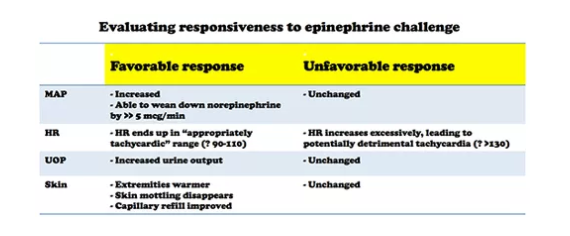 Practical Vasopressors And More In Septic Shock Help From Drs Farkas Weingart And Others Tom Wade Md
Practical Vasopressors And More In Septic Shock Help From Drs Farkas Weingart And Others Tom Wade Md
 Septic Shock Echo Based Goal Directed Algorithm To Monitor Download Scientific Diagram
Septic Shock Echo Based Goal Directed Algorithm To Monitor Download Scientific Diagram
 Vasopressors In Septic Shock Which When And How Much Shi Annals Of Translational Medicine
Vasopressors In Septic Shock Which When And How Much Shi Annals Of Translational Medicine
 Practical Vasopressors And More In Septic Shock Help From Drs Farkas Weingart And Others Tom Wade Md
Practical Vasopressors And More In Septic Shock Help From Drs Farkas Weingart And Others Tom Wade Md
 Shock And Vasopressors State Of The Art Update Springerlink
Shock And Vasopressors State Of The Art Update Springerlink
Plos One Vasopressors For The Treatment Of Septic Shock Systematic Review And Meta Analysis
 Reconsidering Vasopressors For Cardiogenic Shock Chest
Reconsidering Vasopressors For Cardiogenic Shock Chest